Research
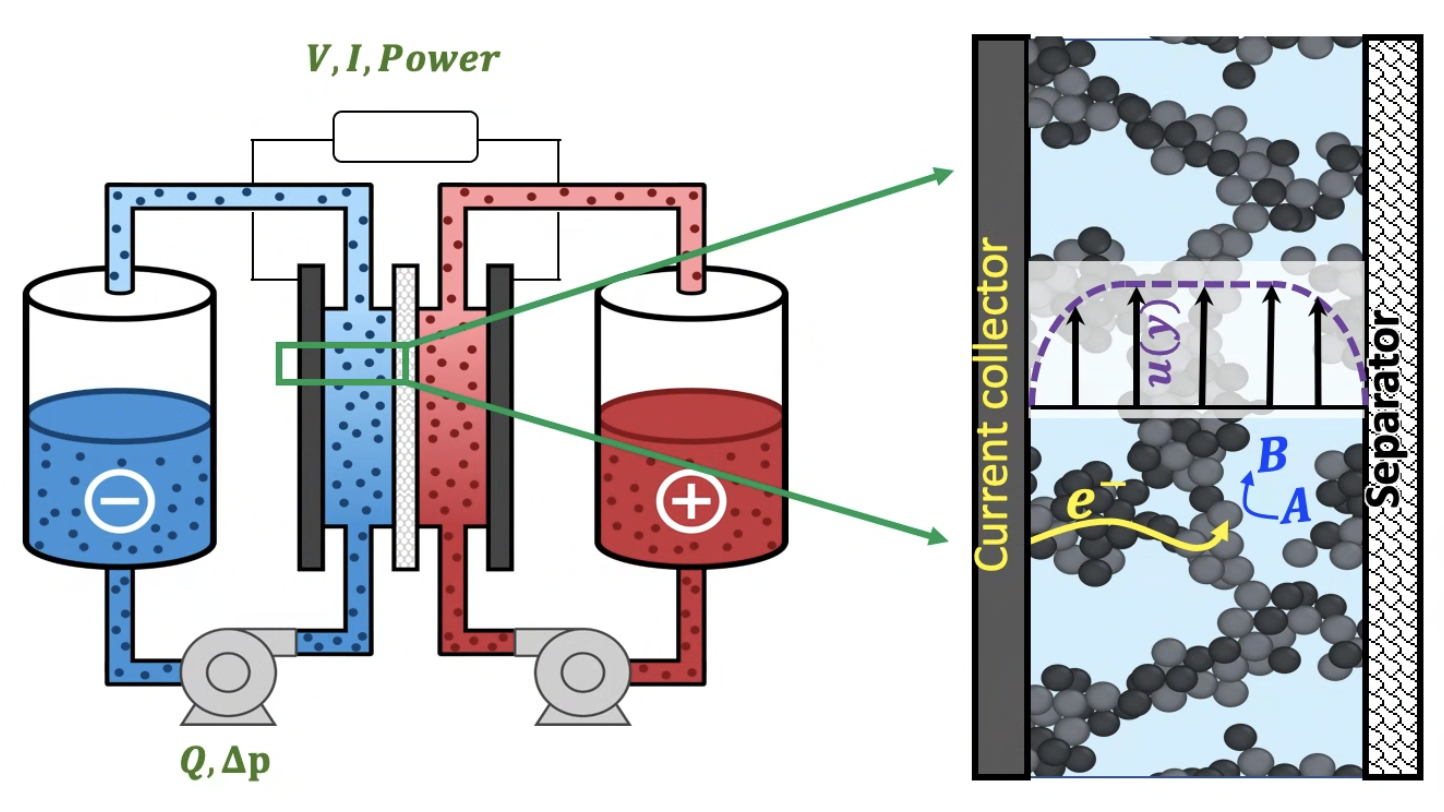
Establishing design rules for electrochemical reactors with slurry electrodes
When slurries of conductive particles flow through electrochemical reactors, multiple coupled processes are at play: flow of non-Newtonian materials, charge tranpsort across slurries and electrochemical kinetics. The reactor performance depends on a vast set of input paraemters related to these processes. We are investigating which set of materials and operating conditions gives raise to optimum reactor performace for applications in energy storage, electrochemical manufacturing and water treatment.
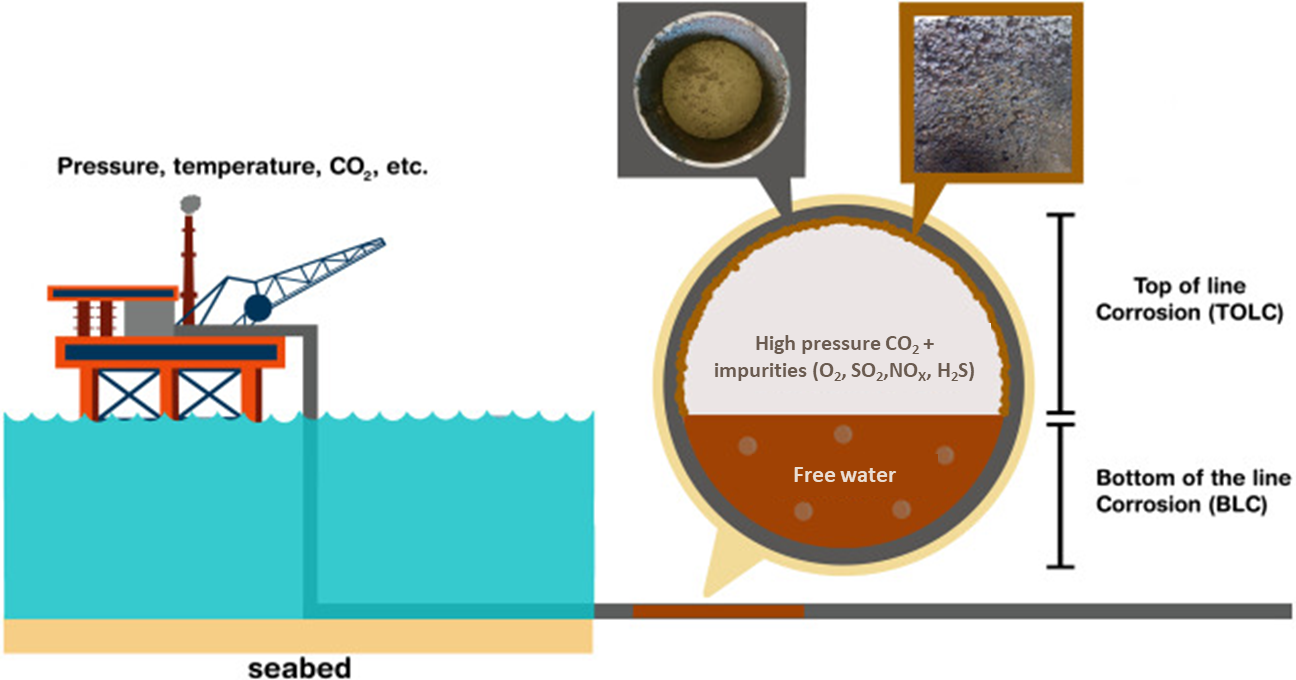
Developing predictive Models for multiphase flow and corrosion in CO₂ transport pipelines
CO₂ transport pipelines are used to move carbon dioxide from capture sites to points of use or storage. They play a key role in carbon capture and storage (CCS) by delivering CO₂ to geological storage sites such as depleted reservoirs or saline aquifers. These pipelines are also critical for enhanced oil recovery (EOR), where CO₂ is injected into oil reservoirs to improve extraction efficiency. In addition, pipelines supply CO₂ for industrial applications, including chemical production, food and beverage carbonation, and dry ice manufacturing. Operating at high pressures, these lines may contain water, which can form carbonic acid and cause pipeline corrosion. We are integrating thermodynamic data, multiphase flow modeling, and electrochemistry to investigate corrosion rates in CO₂ transport pipelines.
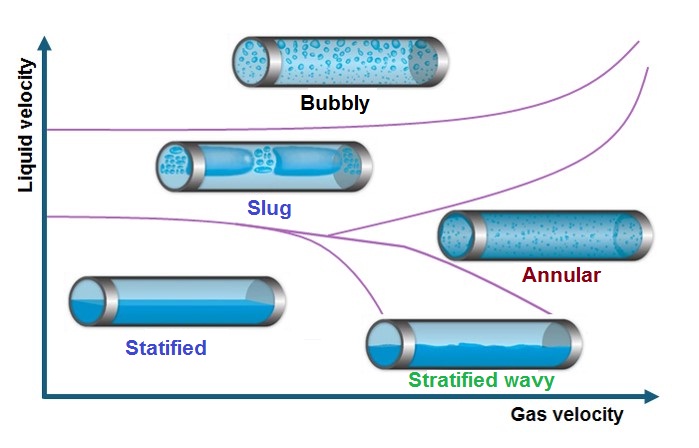
Investigating corrosion rates in various multiphase flow regimes in oil and gas pipelines
Oil and gas pipelines transport mixtures of natural gas, liquid hydrocarbons, and water. The water content can vary widely, from just a few parts per million in dehydrated natural gas to as high as 90 percent by volume in fracking flow lines, depending on the type of pipeline and stage of production. Variations in the composition of gas and liquid phases give rise to diverse flow regimes within the pipelines. Water wetting of the pipe’s internal surface, particularly in the presence of salts and acidic components, can lead to corrosion. In this work, we investigate the effect of different flow regimes and water contents on the rate of pipeline corrosion.